 www.frogfish.ch
www.frogfish.ch

Reproduction
Reproduction:
Mating Behavior - Brood
care - Baby Frogfishes
- Luring - Growing
up
Print version frogfish
behavior - Diese Seite in
Deutsch
Mating Behavior
There are no means to differ the male and female frogfish, for example by coloration or size except by examining the gonads by dissection.
The following photos show the courtship and spawning behavior of several species of frogfishes. About 8 to 12 hours prior to spawning, the female begins to fill up with eggs (40'000 to 180'000 eggs). The eggs measure around half a millimeter. This proceeds at a rapid rate so that shortly before spawning she is so distended, it is hard for her to maintain her position on the bottom. She becomes buoyant (tail up as shown) and is followed around closely by the male. The male continues to nudge the female in the abdomen, and they move quickly to the surface, where spawning occurs. The frogfish may spawn several times over a few weeks. Click on thumbnail for larger photo. Video of Ellen Muller
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video Copyright Mike Bartic
Video Copyright Anne DeLoach
Parenting ends with mating. The thousands of eggs are released encapsulated in a ribbon-like buoyant mass of mucus known as an epipelagic egg raft (gelatinous raft or mucous veil), that drifts for several days crossing large geographical distances and then sinks to the bottom after the embryos hatch. The planktonic stage lasts probably 1 to 2 months. Even small larvae of 5 to 10mm have a lure. Larvae are typically deep bodied (see Antennariidae p. 728ff PDF) and have a large head.
Juvenile frogfish look like smaller versions of their adult forms, but some show special defensive colors (see Baby Frogfishes).
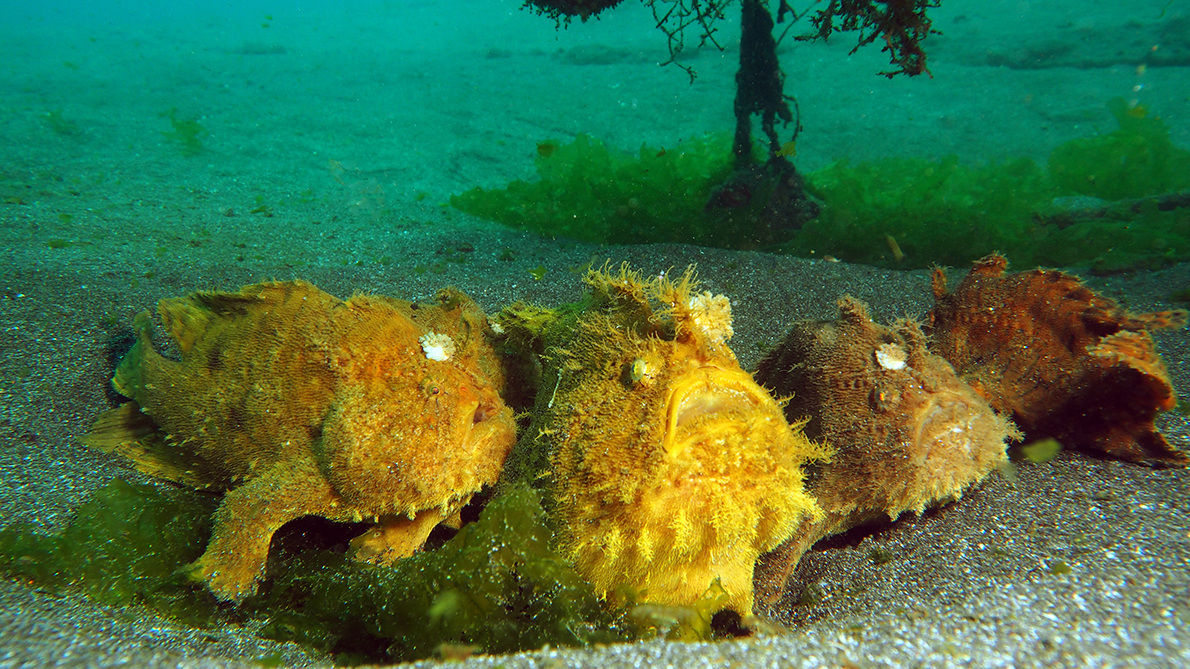

An amazing photo of four A. hispidus sitting next to each another. Probably they were gathering
for mating, since usually they are solitary.
Copyright Niki Weidinger (Gilimanuk, Bali)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brood care
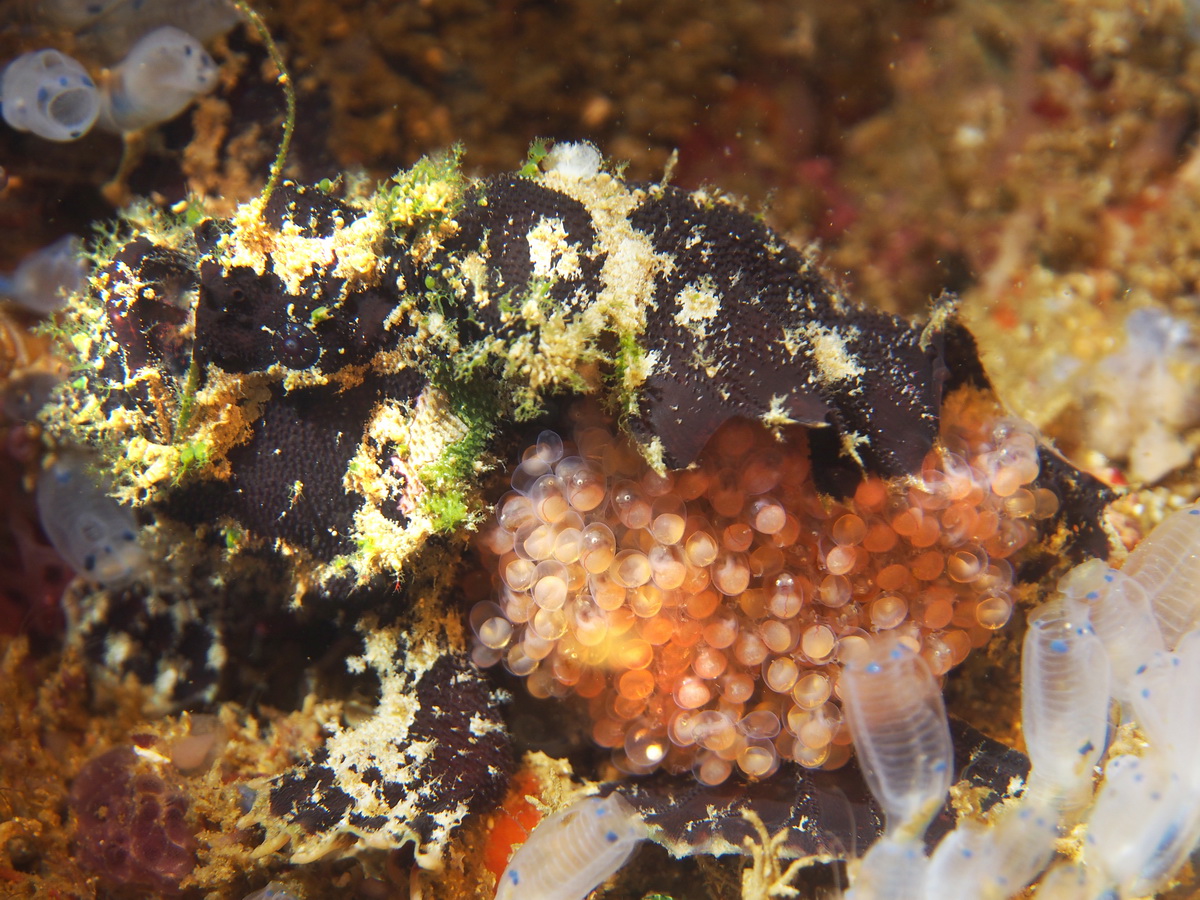

Marble-mouth frogfish (Lophiocharon lithinostomus) with eggs where the small nearly completely developed babies are clearly visible
Copyright Teresa Zubi 2016
A few frogfish species (mostly living in Australia) show special parental care for their eggs. For example Lophiocharon trisignatus or Lophiocharon lithinostomus have fewer but larger eggs than other frogfish species. The female attaches a cluster of eggs with a threadlike structure to the surface of his body (see below) and carries them around until they hatch.
One of the mating pair of Phyllophryne scortea (see photo) and Echinophryne crassipina (see photo) stays close to guard their eggs. Would-be predators lured into the range by the embryos are known to be eaten by the parent frogfish!
Histiophryne cryptacanthus and H. bougainvilli hide the cluster of eggs in a pocket formed by the pectoral fin and the tail which is bent around.
Several courting males of Rhycherus filamentosus gather around the gravid female. Females lay about 5000 eggs in a large mass. The egg mass consists of numerous single-egg strings attached to a gel disc of about 30mm in diameter. The disc is laid first, the long strings of eggs, each on a long sticky double filament. As the male releases sperm, the female fans the eggs with the caudal fin and posterior sides, trying to spread them out into the back of the cave. During this process the male is expelled. Sticky threads entangle themselves with the surrounding growth on rocks. The female then covers the eggs completely with her side and guards them. The young hatch after about 30 days and settle in crevices at the bottom (personal observations by Rudie H. Kuiter).
These frogfish species have relatively few but large eggs and the hatchlings are also relatively large and well developed. The result of this reproduction mode is, that these species have a narrow geographic distribution compared to other frogfish species.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The eggs of Tetrabrachium ocellatum (Four-armed frogfish or Humpback anglerfish) are wrapped around the dorsal fins which are specially hooked. Since a lot of fish like to eat eggs, these eggs might enhance considerably the overall luring effect of a frogfish.
Probably it is very difficult for frogfishes to find a partner in the deep sea. That is why the deep-sea angler (Families Ceratiidae, Caulophrynidae, Photocorynidae, Linophrynidae and Melanocetidae) shows a very strange sexual dimorphism. The male specimen is very small and attaches itself to the body of the female. The teeth and the jaw recede and the blood circulating of the two animals become one. The male frogfish spends the rest of his life attached to the female, like a parasite.
![]()
Baby Frogfishes
Click here for videos of baby frogfishes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The juvenile clown frogfish (Antennarius maculatus) and the juvenile giant frogfish (Antennarius commerson) are said to mimic a distasteful flatworm, complete with undulating dorsal fins to simulate the swimming worm. I think there are also examples of distasteful nudibranchs that look similar. Other frogfish species (Antennarius hispidus, Antennarius striatus) are just specially well camouflaged and look like algae covered rocks or like a slug.
Frogfishes are not poisonous but sometimes inflate their body by swallowing water so they can't be swallowed due to its increased girth.
|
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
Luring behavior in small frogfishes
I have observed, that the juvenile clown frogfish is luring by moving its second dorsal spine instead of its rod and lure. Other juvenile frogfishes seem to lure more frequently than the adult frogfishes. I think this is because they are too small to be mistaken by their prey for a sponge or a algae covered stone, so they have to be more active in luring. Their lure is also larger in comparison with their body size and if you have a magnifying glass or a macro camera you can see it quite well.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Especially the larger frogfish species change the way they hunt while growing. Young frogfishes hide a lot (like the smaller frogfish species). When they are grown up large frogfishes (Antennarius commerson, Antennarius multiocellatus) stay at the same place for a long time on exposed areas in the coral reef , so you will find them there during several dives.
![]()
Growing up
The photos below show the Warty Frogfish (Antennarius maculatus) in different sizes (pictures taken over 3 weeks )
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following pictures were taken over 7 weeks at a dive site in Ankermis Bay, Maumere, Flores, Indonesia. Photos Copyright Heinz Weigel.
|
|
|
|
|
|




































































































