 www.frogfish.ch
www.frogfish.ch

Characteristics
Frogfish Terms
- Esca and illicium
Print version frogfish
behavior - Diese Seite in Deutsch
![]()
The Frogfish
The family of frogfish (Antennariidae =antenna bearers) comprise 13, perhaps 14 genera (Allenichthys, Antennarius, Antennatus, Echinophryne, Fowlerichthys, Histiophryne, Histrio, Kuiterichthys, Lophiocharon, Nudiantennarius, Phyllophryne, Rhycherus, Tathicarpus) with 52 (54?) known species. Check out frogfish taxonomy and phylogenetic relationships.
Frogfishes are relatively small fishes, the largest ist about 38cm (F. ocellatus), but there are quite a few small species around 5 to 10 cm large. Some species can be of many different colours, from black to red, orange, yellow, browns, white, purple, green, some even have patches of blue. The colours usually help them to mimicry their environment such as sponges, corals and algae.
![]()
Frogfish Terms
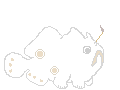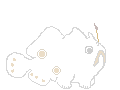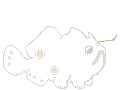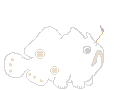
Small stocky globose fishes (5-40cm). Loose prickly skin, limb-like pectoral fins with an elbow-like joint, small round gill openings behind the fins (not covered by plates), very large upward directed mouth. The pectoral fins are modified and look like feet, including small toes.
First dorsal spine is modified into a moveable fishing
rod or luring apparatus (illicium) tipped with a fleshy lure or bait (esca).
The rod or stalk comes in different lengths and is sometimes striped.
The third dorsal fin is greatly enlarged.
Click on thumbnail for larger photo.
![]()
Esca and illicium
The shape of the lure is one of the main distinguishing marks that will even help a layman to identify a frogfish. The lure often but not always mimics a small animal. The lures of some species (Antennarius striatus or Antennarius hispidus) are shaped like a worm, others (Antennarius commerson or Phyllophryne scortea) like a shrimp or even like a small fish with eye-spot and appendages resembling fins (Antennarius maculatus). While using the lure the frogfish even imitates the way which that particular animal would move. Using mimicry to catch prey is called aggressive mimicry. Click on thumbnail for larger photo.
|
|
|
|
|
|








